Intraoperative neuromonitoring is used to monitor the central nervous system during neurosurgery operations to lower the risk of postoperative problems.
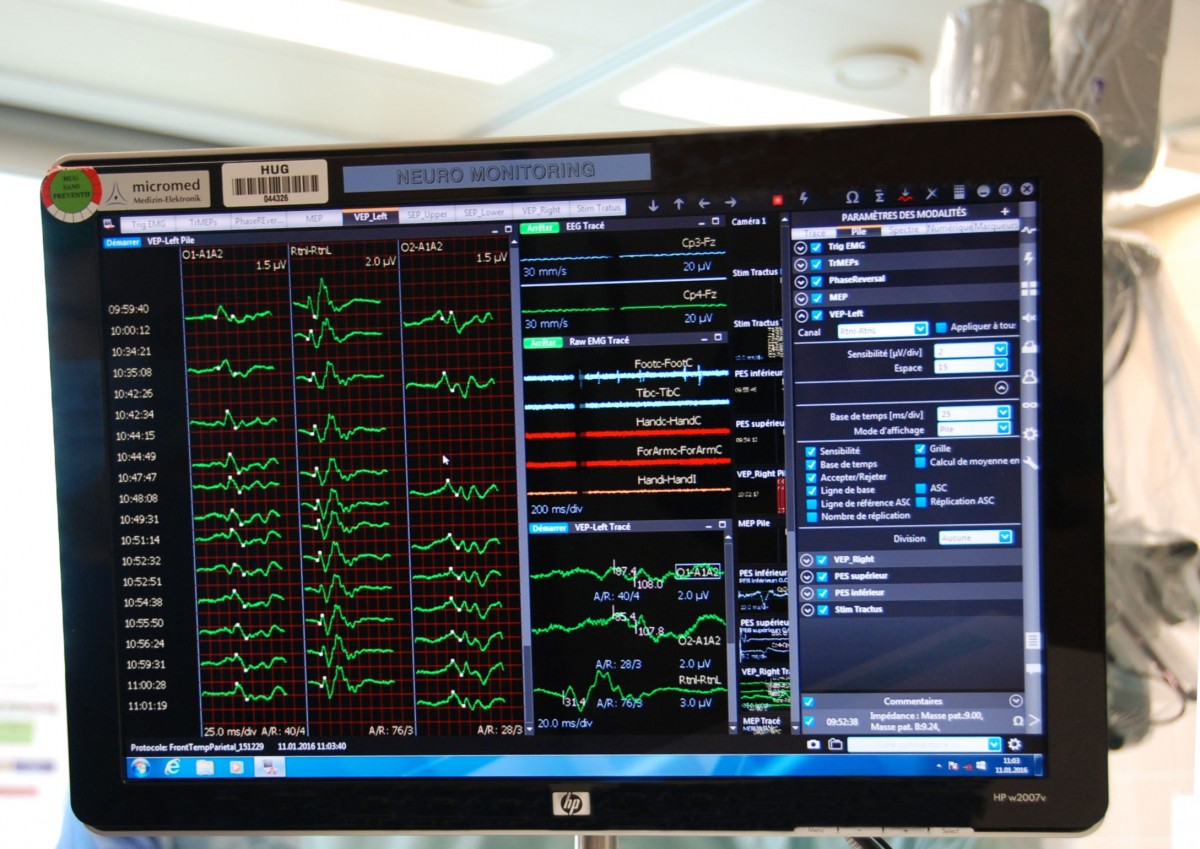
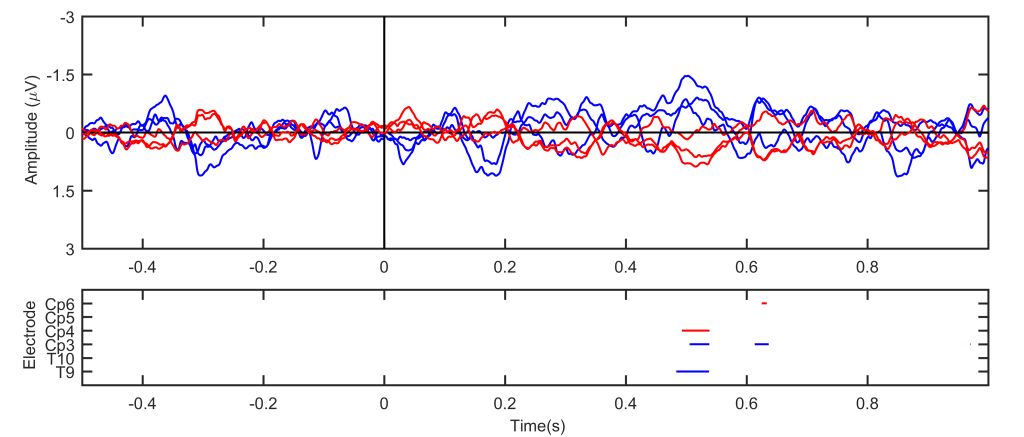
Essential functions, including motor, somatosensory, auditory or visual functions, can be monitored throughout the surgical procedures.
These neurophysiological actions, which are carried out continuously, detect early changes due to modifications of the nervous system that are still reversible. This is to alert the surgeon so that they can adapt their operating strategy to avoid a neurological deficit.
Intraoperative neuromonitoring also provides methods to locate functional areas and pathways.