Evaluate your cardiovascular risk
See Automatic cardiovascular risk calculator
7 Cardiovascular Risk Factors
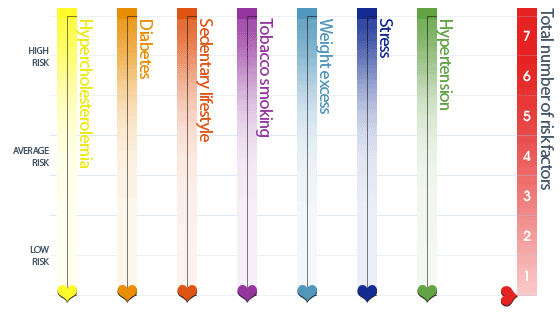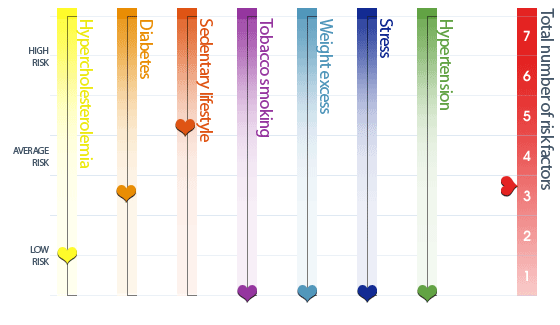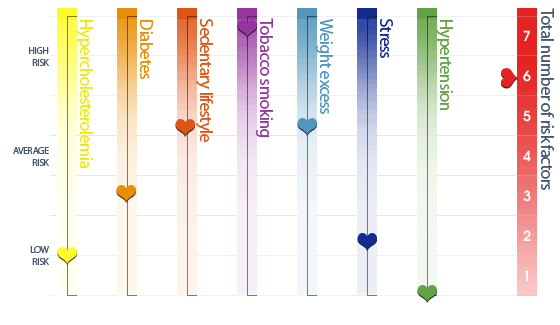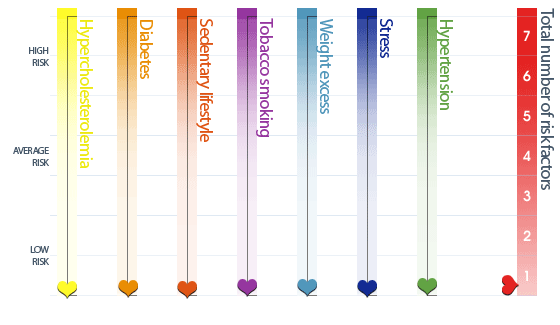
How do your analysis results, for each risk factor, compare to normal values?
Adjust each cursor according to the corresponding normal values.
Identification of Particularly Risky Situations
- Coronary artery disease/known or established atherosclerosis
- Diabetes
All diabetic patients are considered to be particularly at risk, and this even though in the case of well balanced type I diabetes with no secondary complications, the cardiovascular risk is only slightly higher than in the non-diabetic population. - Familial hyperlipidemia (hypercholesterolemia)
- Metabolic syndrome - Diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome:
- At least three of the following criteria have to be filled:
- Waist circumference > 102 cm for men, > 88 cm for women
- Fasting triglycerides = 1.7 mmol/l
- HDL-cholesterol <1.0 mmol/l for men, <1.3 mmol/l for women
- Systolic blood pressure = 130 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure = 85 mm Hg
- Fasting blood glucose = 6.1 mmol/l (= 5.6 mmol/l according to the ADA (American Diabetes Association))
Normal values
- Blood pressure : Less than 140/90 mm Hg
If diabetic: less than 135/85 mm Hg
- Glycemia (blood sugar) (normal) : Fasting : between 4 and 5.5 mmol/l, 2h after a meal (post prandial): less than 7.7 mmol/l
If diabetic: fasting: between 5.6 and 6.8 mmol/l, 2h after a meal (post prandial): between 7.8 and 11 mmol/l
- Lipids
- LDL-cholesterol:
- High risk patients³ (> 20%): < 2.6 mmol/l (If you have had a heart attack or have atherosclerosis, you are in a high risk category)
- Intermediate risk patients (10 - 20%): < 3.4 mmol/l
- Low risk patients (> 10%): < 4.1 mmol/l
- Patients with no cardiovascular risk factors: 4.9 mmol/l
- Triglycerides
- TG > 1.7 mmol/l: treatment if diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
- TG > 5.0 mmol/l: treatment in all cases
- TG > 10.0 mmol/l (VI): Main objective: avoid acute pancreatitis, consultation with lipid specialist
- HDL-cholesterol
- If levels are low: increase levels of HDL-cholesterol (no target levels) by improving lifestyle: abstinence from tobacco, physical exercise, weight loss if overweight or obese.
- LDL-cholesterol:
- Obesity
- Obesity: BMI above 30 kg/m2
- Overweight: BMI between 25-30 kg/m2
- Waist circumference
Should be less than 102 cm for men, 88 cm for women
- Sedentary lifestyle
A sedentary person is someone who has less than 30 minutes of moderately intense physical activity per day (e.g., rapid walking)
- Cigarette smoking
Smoker or non-smoker
- Stress
Difficult to evaluate normal level